Wi-Fi networks use radio signals, it transmits at frequencies of 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz. Each frequency band has its advantages and disadvantages, and we will see which is the most convenient to use depending on your situation, speed, distance, and device.
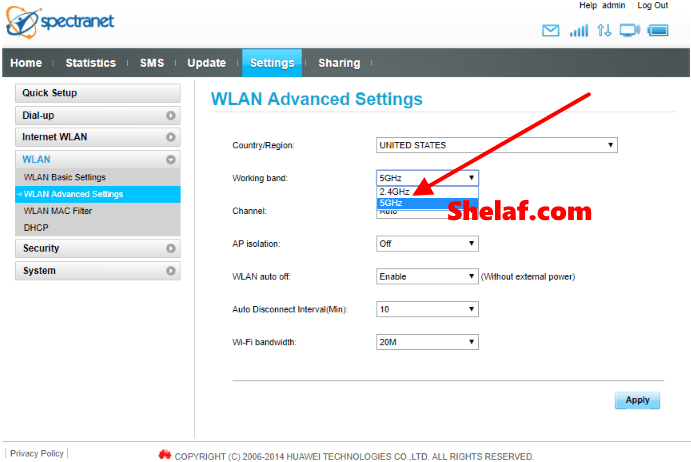
All modern Wi-Fi devices support 2.4 GHz connections, while some supports both frequency band. Home broadband routers that feature both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radios are called dual-band wireless routers.
An important distinction to make is between a WiFi network and your mobile phone’s wireless network. These are two very different technologies, and it can become even more confusing when you discuss 5 GHz WiFi frequency band and 5G mobile networking technology, the replacement for 4G.
Contents
5G & 5 GHz Are Different: Here’s What They Mean
Here we will discuss WiFi networking that you can set up in your home using a router, and the two frequency bands used and how a dual-band home network can be set up to take maximum advantage of the best of both frequencies. This does not cover mobile networking technology for smartphones and other devices.
GHz and Network Speed
WiFi networking comes in a few varieties. These WiFi standards define improvements in networking technology. The standards are (in order of release, oldest to newest):
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g
802.11n
802.11ac
These standards are connected to GHz band frequencies, but these aren’t discussed in great detail here, but they are referred to.
A 5 GHz network can carry more data than a 2.4 GHz network and so technically are faster (assuming the electric power to the higher frequency radio is maintained at a higher level). 5GHz radios support significantly higher maximum data rates in network standards 802.11n and 802.11ac. Home devices that generate or consume the largest amount of network traffic, like video streaming units or game consoles, generally run fastest over 5 GHz links.
GHz and Network Range
The higher the frequency of a wireless signal, the shorter its range. 2.4 GHz wireless networks therefore cover a substantially larger range than 5 GHz networks. In particular, signals of 5 GHz frequencies do not penetrate solid objects nearly as well as do 2.4 GHz signals, limiting their reach inside homes.
GHz and Network Interference
You may notice that some cordless phones, automatic garage door openers, and other home appliances also use 2.4 GHz signaling. Because this frequency range is commonly used in consumer products, it’s become saturated with signals. This makes it more likely that a 2.4 GHz home network will suffer interference from appliances than will a 5 GHz home network. This can slow down and interrupt WiFi network speed in these cases.
All these interferences do not affect the 5 GHz being very far from that band, which also has the advantage of being able to send data through several channels at the same time. Thanks to all this, a 5 GHz signal is more stable and reliable, but in general, it has a shorter range. Therefore, using the 2.4 GHz Wifi has only one advantage: that it reaches a greater distance if the router is several tens of meters away from our device, or if there are walls in between.
With this, we have the 2.4 GHz WiFi from the 2.412 MHz bands (channel 1) to the 2.472 MHz (channel 13), where there is a new channel in every 5 Mhz. Each channel covers up to 22 MHz, where they overlap each other, hence, in the case of the 5 GHz WiFi, there are 21 channels of 20 Mhz each, wherein that space none overlap each other.
The actual maximum speed reached by the 2.4 GHz coverage is about 150 Mbps (theoretical 300 Mbps), while at 5 GHz it reaches speeds that vary between 200 Mbps and 1 Gbps, with theoretical maximums of 433 Mbps and 1 or 7 Gbps.
However, the fact is that the most modern routers can now join both networks into one, in such a way that it automatically decides which network is the most convenient to use at any time, automatically changing our device between them. This is possible simply due to the features like Intelligent WiFi, present in routers such as the premium WiFi Repeater.
Even if they do not have Intelligent WiFi, almost all current routers create two networks, and the mobile automatically connects to the 2.4 GHz one if we are connected to the 5 GHz and we are left without coverage.
You can also give the same name and password to both networks, although this may not work with all devices. You should bear in mind that some of your old devices may only work with 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, as on the smartphones more than 5 years ago.
GHz and Cost
Some people mistakenly believe 5 GHz network technology is newer or somehow more innovative than 2.4 GHz because 5 GHz home routers generally became available after those that use 2.4 GHz radios. In fact, both types of signaling have existed for many years and are both proven technologies.
Routers that offer both 2.4GHz and 5GHz radios are generally more expensive than those offering only 2.4GHz radios.










1 thought on “Here’s Why You Should Use 5GHz Wi-Fi Band in Place of 2.4GHz”
thanks alot. Check out Naijabuz